Future of Technology in Healthcare sector
The future of healthcare technology is promising, as it transforms disease detection, diagnosis, and treatment, improving care quality and accessibility. Here are some of the major trends that are shaping the future of healthcare technology:
Artificial intelligence (AI): AI is improving decision-making, personalized therapy, and diagnosis, while also reducing costs, optimizing workflows, and automating tasks. It can detect skin, lung, and breast cancers using pictures, x-rays, and mammograms.
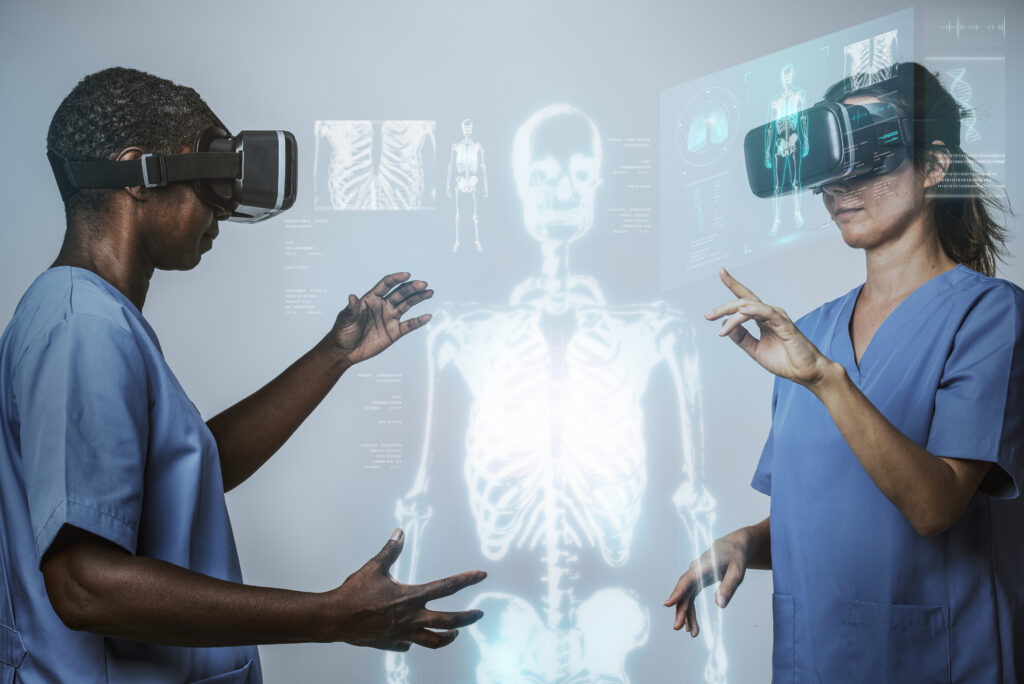

Data analytics: Data analytics involves gathering, evaluating, and interpreting vast data to improve results, predict risks and opportunities, and identify patterns, trends, and correlations. It aids in managing chronic illnesses, avoiding readmissions, and maximizing resource use.
Data interoperability: It refers to the seamless exchange and use of data across devices and systems, enhancing patient satisfaction and facilitating better care coordination, such as telemedicine, remote monitoring, and electronic health records.
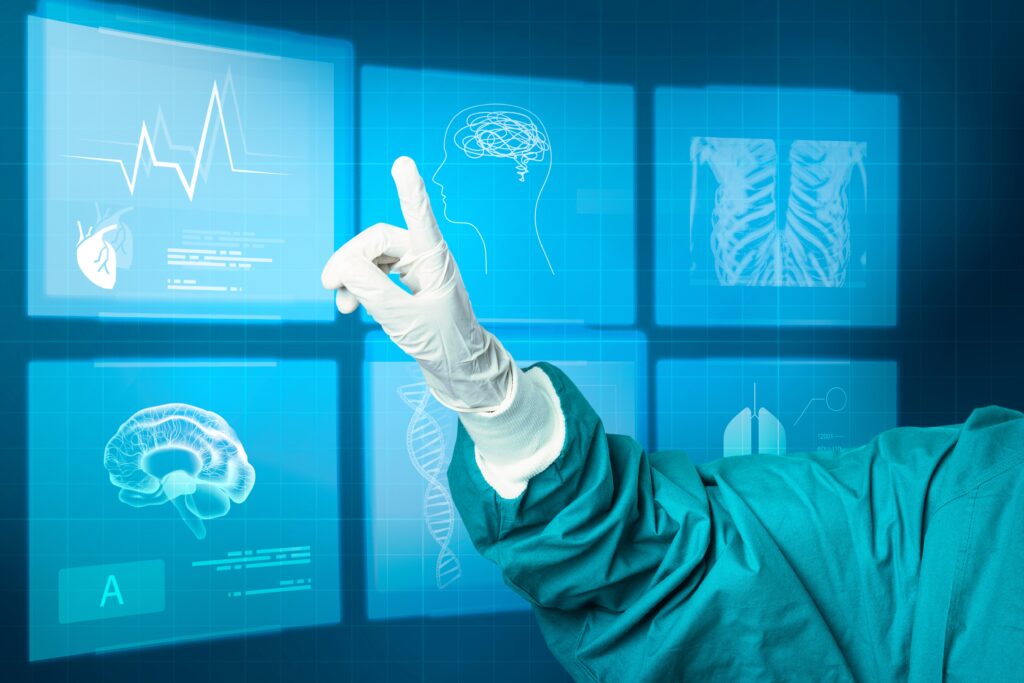

Virtual assistants: Using voice recognition and natural language processing, assist patients and medical professionals by providing information, direction, and support, such as appointment scheduling, prescription reminders, and general question-answering.

Blockchain: Blockchain technology, a distributed ledger, can enhance data security, transparency, and trust in the healthcare industry by facilitating data sharing, preventing fraud, and protecting patient privacy.
Wearable devices: Wearable technology, which can be attached to clothing or worn on the body, can track health and fitness metrics like heart rate, blood pressure, and activity levels, providing recommendations, notifications, and feedback to support wellbeing, manage chronic diseases, and motivate healthy behavior.

Artificial limbs: Also known as prosthetics, replace missing or impaired body parts, enabling people with disabilities or injuries to regain mobility and independence. They come in various types, including arm, leg, hand, foot, and cosmetic prosthetics, and vary in design, material, and technology.

These are the some major trends in healthcare technology are revolutionizing the future by creating new opportunities, addressing pressing challenges, and improving global health and well-being, while also creating new possibilities for the sector.
What are some challenges of implementing technology in healthcare?
The implementation of technology in healthcare presents numerous advantages, but also presents several challenges, including:

- Security: Strong encryption, authentication, and data protection procedures are necessary since healthcare apps frequently handle sensitive and private patient data. Cyberattacks and security lapses can jeopardise patient confidentiality and confidence, as well as result in negative legal and financial outcomes.
- Cost-effectiveness and integration: Healthcare devices and systems must be able to work together as well as with emerging technologies like WebRTC and cloud computing. But because of outdated technologies, problems with browsers, limitations on the network, and expensive prices, this can be challenging.
- Onboarding and training: To use new technology successfully and efficiently, administrators and healthcare professionals need to be supported and trained. But because of hectic schedules, intricate workflows, and opposition to change, this can be difficult.
- Data integrity and compliance: Healthcare technology must abide by a number of laws and rules, including CMS, GDPR, and HIPAA. Ensuring data accuracy, quality, and consistency is necessary for this, as is adhering to ethical and professional norms.
These are a few of the primary obstacles to using technology in healthcare. Healthcare companies must take a proactive and cooperative approach to overcoming these obstacles, include users, vendors, and stakeholders in the development, testing, and assessment of new technology. Along with security, integration, and compliance solutions, they also need to spend in staff education, training, and support. By doing this, they will be able to fully utilise technology to raise the standard, accessibility, and cost of healthcare.
What is the role of telemedicine in healthcare?
 Telemedicine, the use of technology to provide healthcare services and information remotely, can enhance healthcare quality, accessibility, and affordability, particularly for those in remote areas with limited mobility or other barriers, while also aiding disease prevention, cost reduction, and patient satisfaction.
Telemedicine, the use of technology to provide healthcare services and information remotely, can enhance healthcare quality, accessibility, and affordability, particularly for those in remote areas with limited mobility or other barriers, while also aiding disease prevention, cost reduction, and patient satisfaction.
Some of the roles of telemedicine in healthcare are:
- Offering diagnosis and treatment: By utilising gadgets like computers, tablets, smartphones, and sensors, telemedicine can let medical professionals assess, diagnose, and treat patients at a distance. In addition to lowering the danger of exposure and infection, this can save time and money.
- Monitoring and managing chronic conditions: Wearable technology, applications, and internet platforms can be used by patients with chronic conditions including diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease to monitor and manage their health at home. In addition to lowering problems and hospital stays, this can enhance adherence, results, and quality of life.
- Promoting and educating people about health:
- Online courses, podcasts, blogs, and videos are just a few of the tools and resources that telemedicine may make available to patients and healthcare professionals. This can support healthy behaviours and lifestyles and help raise health literacy, awareness, and empowerment.
- Aiding in emergency and disaster response: In times of pandemics, earthquakes, and floods, telemedicine can assist in providing prompt and efficient medical treatments as well as coordination. This can lessen pain, save lives, and increase resiliency.
These are a few of the ways telemedicine is used in medicine. The discipline of telemedicine is one that is growing and changing quickly, with the potential to completely change how people get and use healthcare.
What are some examples of telemedicine?
Some examples of telemedicine are:
- Virtual consultations: These take place over the
 phone, over text, or by video, and do not require an in-person meeting between the patient and the healthcare professional. For instance, a patient can discuss their symptoms, medication, or test findings with their doctor to get guidance on diagnosis and course of treatment.
phone, over text, or by video, and do not require an in-person meeting between the patient and the healthcare professional. For instance, a patient can discuss their symptoms, medication, or test findings with their doctor to get guidance on diagnosis and course of treatment. - Remote monitoring: This refers to the process of gathering and sending a patient’s medical information—such as blood pressure, heart rate, glucose level, or oxygen saturation—to a healthcare professional via gadgets, applications, or internet platforms. For instance, a diabetic patient can measure their blood sugar with a glucometer and email the results to their physician for assessment and comment.
- Telepharmacy: This refers to the use of technology to provide patients with pharmacy services, such as prescription filling, refills, counselling, or education, without the need to visit a physical pharmacy. For instance, a patient can use a video conference to consult with a chemist regarding their medication or order their medication online and have it delivered right to their home.
- Telepsychiatry: This refers to the use of technology to provide mental health services to patients without requiring them to visit a mental health facility, such as assessment, diagnosis, therapy, or medication management. For instance, a depressed patient can utilise a chatbot to get emotional support or an app to arrange and attend online sessions with a therapist.
- Teledermatology: In this context, a patient can use technology to obtain dermatological services, such as skin examination, diagnosis, treatment, or referral, without having to see a dermatologist. A patient with a skin rash, for instance, can take a picture of their skin with their smartphone and email it to a dermatologist for assessment and advice.
These are a few telemedicine examples that can enhance healthcare accessibility, affordability, and quality.
The Future of nanotechnology in healthcare
 manipulating matter at the nanoscale, has numerous applications in healthcare. It can improve disease diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and enhance the quality and accessibility of healthcare services. Nanotechnology is shaping the future of healthcare by enhancing the quality and accessibility of healthcare services.
manipulating matter at the nanoscale, has numerous applications in healthcare. It can improve disease diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and enhance the quality and accessibility of healthcare services. Nanotechnology is shaping the future of healthcare by enhancing the quality and accessibility of healthcare services.
- Nanomedicine: This field of study uses
 nanotechnology to develop innovative medications, medical equipment, and therapeutic treatments that specifically target particular body tissues, cells, or organs. medication resistance can be defeated, side effects can be minimised, and medication delivery can be improved with the use of nanomedicine. Using nanoparticles that can deliver chemotherapeutic medications, heat, or radiation to the tumour cells while preserving the healthy cells is one way that nanomedicine can help treat cancer.
nanotechnology to develop innovative medications, medical equipment, and therapeutic treatments that specifically target particular body tissues, cells, or organs. medication resistance can be defeated, side effects can be minimised, and medication delivery can be improved with the use of nanomedicine. Using nanoparticles that can deliver chemotherapeutic medications, heat, or radiation to the tumour cells while preserving the healthy cells is one way that nanomedicine can help treat cancer. - Nanodiagnostics: This refers to the application of nanotechnology in the identification and tracking of illnesses, infections, or biomarkers within the body. Nanodiagnostics can lower testing costs and invasiveness while simultaneously increasing diagnosis speed, accuracy, and sensitivity. By employing nanosensors to detect the presence of bacteria, viruses, or antigens in blood, saliva, or urine samples, for instance, nanodiagnostics can assist in the diagnosis of infectious disorders.
- Nanobots: These tiny robots can carry out a variety of functions inside the body, including disease-destroying, drug-delivery, and tissue repair. DNA, enzymes, or logic gates are examples of internal mechanisms that can control nanobots, as well as external signals like magnetic fields, light, or sound. Glucose-responsive nanogels, which release insulin when necessary, are one way that nanobots can help treat diabetes.
- Nanomaterials: Because of their nanoscale composition or structure, nanomaterials are materials with unique properties or uses. Biomaterials, implants, and other devices that can communicate with the body’s biological systems can be developed using nanomaterials. For instance, nanofibers, nanoscaffolds, or nanocapsules that promote cell proliferation, differentiation, or migration can be used by nanomaterials to aid in the regeneration of tissues or organs.
These are some of the examples of how nanotechnology is changing the future of healthcare. Nanotechnology is a rapidly evolving and expanding field that has the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered and experienced.
Conclusion
 In summary, technology is still transforming the healthcare industry and bringing about a lot of improvements. Technology is a key factor in determining how healthcare will develop in the future, from boosting medical research and patient care and safety to expediting administrative duties. Healthcare practitioners may now give patients with more individualised and effective care because to advancements in telemedicine, wearable technology, AI-driven diagnostics, and electronic health records. But issues like data protection, technology differences, and the requirement for appropriate training and new technology integration must be addressed. We can create the conditions for a more connected, healthier healthcare system in the future by embracing and appropriately utilising technology.
In summary, technology is still transforming the healthcare industry and bringing about a lot of improvements. Technology is a key factor in determining how healthcare will develop in the future, from boosting medical research and patient care and safety to expediting administrative duties. Healthcare practitioners may now give patients with more individualised and effective care because to advancements in telemedicine, wearable technology, AI-driven diagnostics, and electronic health records. But issues like data protection, technology differences, and the requirement for appropriate training and new technology integration must be addressed. We can create the conditions for a more connected, healthier healthcare system in the future by embracing and appropriately utilising technology.
Read our blog “Future of EVs in India“